void가 아닌 함수에서의 반환 값이 없다는 것은 코드 자체를 잘못 짠 것이다.
그런 코드는 이상하게 작동할 수 있다.
이 코드는 사용자가 yes를 입력했다면 "긍정적인 답변" 이 출력되고, no를 입력했다면 "부정적인 답변"이라고 출력되게 하는 코드이다.
조건은 get_response 함수에서 yes면 1을 반환하고 no면 0을 반환하도록 하는 것이 조건이다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
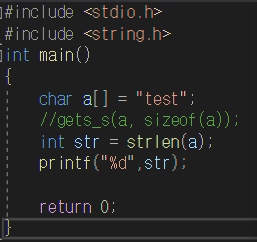
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int get_response(char* prompt);
int main(void)
{
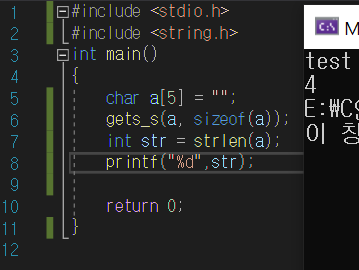
char a[5] = "";
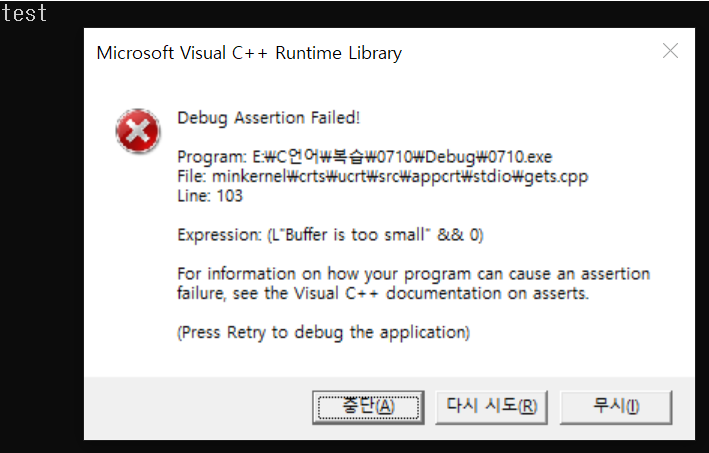
gets_s(a, sizeof(a));
int b = get_response(a);
if (b == 1)
{
printf("긍정적인 답변");
}
else if (b == 0)
{
printf("부정적인 답변");
}
else
{
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
int get_response(char* prompt)
{
char a[] = "yes";
char b[] = "no";
if (strcmp(prompt, a) == 0)
{
return 1;
}
else if (strcmp(prompt, b) == 0)
{
return 0;
}
}
|
cs |
이런식으로 코드를 짰다면 get_response 함수에서 사용자가 yes나 no말고 다른것을 입력했을 때
반환 값이 없다. // 잘못 짠 코드
이런식의 코드는 실행은 되는데 이상하게 작동했다.
예를들어 y만 입력해도 "긍정적인 답변" 이라고 나오고 nod 이런식으로 입력해도 "긍정적인 답변" 이라고 나온다.
그래서 get_response 함수에서 else 를 하나 추가해줬다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int get_response(char* prompt);
int main(void)
{
char a[5] = "";
gets_s(a, sizeof(a));
int b = get_response(a);
if (b == 1)
{
printf("긍정적인 답변");
}
else if (b == 0)
{
printf("부정적인 답변");
}
else
{
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
int get_response(char* prompt)
{
char a[] = "yes";
char b[] = "no";
if (strcmp(prompt, a) == 0)
{
return 1;
}
else if (strcmp(prompt, b) == 0)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return EOF;
}
}
|
cs |
else 를 추가해주니 결과가 정상적으로 나온다.
'<Programming> > <C>' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C언어] 문자열을 정수로 변환하기 (atoi 함수) (0) | 2020.07.17 |
|---|---|
| [C언어] strtok 함수 (0) | 2020.07.16 |
| [C언어] 문자열 (strlen) (0) | 2020.07.10 |
| [C언어] 버블정렬 (0) | 2020.07.07 |
| [C언어] 문자열의 길이를 구해서 출력 | scanf와 gets_s 차이점 (0) | 2020.07.06 |